Building the UI
Contember Interface is a React framework for building fast custom UIs. Contember Engine can work separately as an headless GraphQL API, but together with Interface you can quickly build interface for users that need to work with data right away.
In this example we will create an UI for managing articles. You can use any React components alongside the Interface components. Data binding makes this very easy and fast to build almost any single page application (SPA) imaginable.
Building user interfaces
Before we start, make sure you already have a Contember project running on your computer. This should be a project with your data model that we made in the designing your model guide.
In Interface 1.2 we are introducing new LayoutKit that fully embraces new Scopes. Together with Slots nad Directives it replaces legacy Pages. The upgrade is smooth and it gives you way more power and options how you can build layouts. About new layouts
List all articles
First, we want to create a display for all articles present in our project. To achieve this, we're using the DataGridScope component. This component generates a table, including filters for sorting and searching data.
To start, navigate to admin/pages and create a new file named articleList.tsx.
import * as React from 'react'
import { DataGridScope, TextCell } from '@contember/admin'
import { SlotSources } from '../components/Slots'
const { Title } = SlotSources
export default () => (
<>
<Title>Articles</Title>
<DataGridScope entities="Article">
<TextCell field="title" header="Title" />
</DataGridScope>
</>
)
What we've created here is a page that renders a table listing all the articles in our project. The table includes a column for the title of each article. Let's break down what's happening:
- We begin by importing the
@contember/adminpackage. This package contains all necessary components and also supports TypeScript autocompletion. - We also import the
SlotSourcescomponent namespace from../components/Slotsused to define the title of our page. To learn more about this, see the Slots documentation. - Next, we export the page component as the default export. This is necessary for our routing and navigation.
- We implement the
DataGridScopecomponent to display our data in a simple, easy-to-read grid format. - We specify the entity we want to work with, which in this case is
Article. This entity name should match what we defined in our model. - Lastly, we use the TextCell component to add a text column, designated for the title of each article.
When you navigate to localhost:1480/article-list, you should now see a list of your articles. Keep in mind, this list will be empty if no articles have been added to the data model yet.
Routing
In addition to the steps above, it's important to note how routing works within this framework:
The naming of pages (and by extension, URL paths) is automated. The name given to a page is determined by the name of the file and the function, with slashes ('/') used as separators.
For example, if you have a default export from a file named post.tsx, the resulting page name would be post. If there's a function within the same file that's exported as edit, the page name would be post/edit.
Create an article
Now we're moving on to creating an article. For this, we'll make a new file called articleCreate.tsx.
import * as React from 'react'
import { CreateScope, PersistButton, RichTextField, TextField } from '@contember/admin'
import { SlotSources } from '../components/Slots'
const { Title, Actions } = SlotSources
export default () => (
<>
<Title>Create Article</Title>
<CreateScope entity="Article">
<TextField field="title" label="Title" />
<RichTextField field="content" label="Content" />
<Actions>
<PersistButton />
</Actions>
</CreateScope>
</>
)
- First, we're creating a new file named articleCreate.tsx in the admin/pages directory.
- We're using the
CreateScopecomponent. This component allows us to create new entries for our specified entity - in this case, an Article. - We're defining the entity we're adding, which is Article again.
- We're employing two components to capture user input:
TextFieldandRichTextField. These components are connected to thetitleandcontentfields of ourArticleentity respectively.
By navigating to localhost:1480/article-create, you can now create a new article. When you return to the list of articles, you'll see that your new article has been added.
However, you'll notice the user experience isn't perfect yet. For instance, after creating an article, the application doesn't automatically switch to edit mode. To improve this, let's add an edit page next:
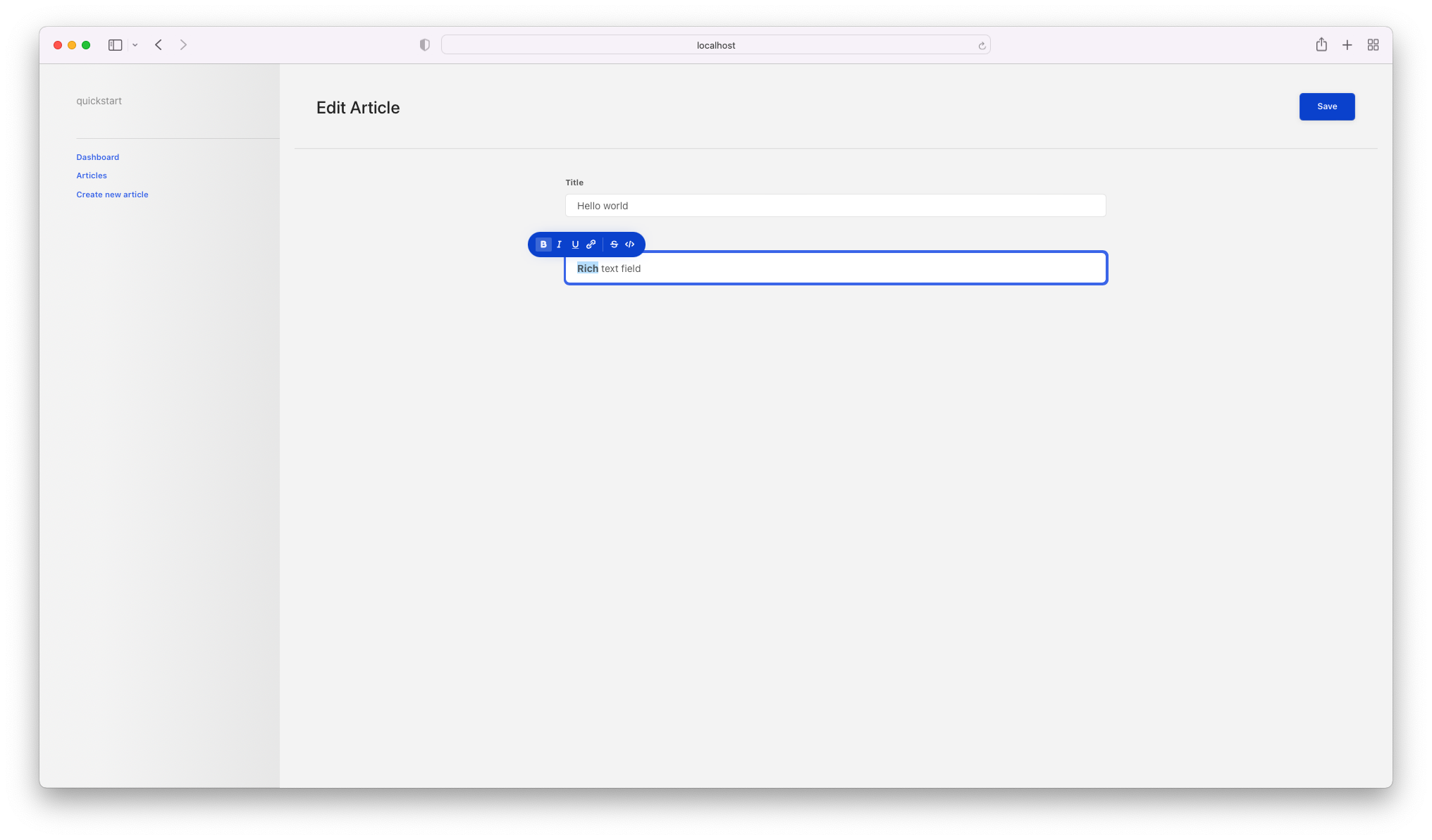
Edit article
Now we're going to tackle editing an article. To do this, we'll create a new page named articleEdit. This page will look quite similar to the create page, but it will be designed to edit an existing article:
import * as React from 'react'
import { EditScope, PersistButton, RichTextField, TextField } from '@contember/admin'
import { SlotSources } from '../components/Slots'
const { Title, Actions } = SlotSources
export default () => (
<>
<Title>Edit Article</Title>
<EditScope entity="Article(id = $id)">
<TextField field="title" label="Title" />
<RichTextField field="content" label="Content" />
<Actions>
<PersistButton />
</Actions>
</EditScope>
</>
)
Here's the breakdown of this code:
- We start by creating a new file named articleEdit.tsx in the
admin/pagesdirectory. - We're using the
EditScopecomponent this time. This component is similar toCreateScopebut it is used for modifying existing entities. - We specify which Article entity we want to edit by providing an id:
Article(id = $id). This id will be dynamically populated based on the article selected for editing. - Like before, we're using
TextFieldandRichTextFieldcomponents to handle editing for the title and content fields respectively.
Now, with this new edit page in place, you'll be able to modify existing articles. So let's use it. We'll redirect users from our create page to the edit page after the article is successfully created.
import * as React from 'react'
import { CreateScope, PersistButton, RichTextField, TextField } from '@contember/admin'
import { SlotSources } from '../components/Slots'
const { Title, Actions } = SlotSources
export default () => (
<>
<Title>Create Article</Title>
<CreateScope
entity="Article"
redirectOnSuccess="articleEdit(id: $entity.id)"
>
<TextField field="title" label="Title" />
<RichTextField field="content" label="Content" />
<Actions>
<PersistButton />
</Actions>
</CreateScope>
</>
)
This is done with redirectOnSuccess prop where we specify link to page where user should be redirected. This is our first encounter with Contember Interface query language. Now if you create a new article you're automatically redirected to the edit page.
More cells in datagrid
Next, let's enhance our data grid with additional cells to open detail, create new or delete an existing article.
import * as React from 'react'
import { DataGridScope, DeleteEntityButton, GenericCell, Link, LinkButton, TextCell } from '@contember/admin'
import { SlotSources } from '../components/Slots'
const { Title, Actions } = SlotSources
export default () => (
<Title>Articles</Title>
<Actions>
<LinkButton to="articleCreate">Add article</LinkButton>
</Actions>
<DataGridScope entities="Article">
<TextCell field="title" header="Title" />
<GenericCell shrunk><Link to="articleEdit(id: $entity.id)">Edit</Link></GenericCell>
<GenericCell shrunk><DeleteEntityButton immediatePersist /></GenericCell>
</DataGridScope>
)
Let's break this down:
- We've added two new
GenericCellcomponents to our data grid. It's just a generic column without any functionality. - The first
GenericCellincludes a Link component. This links to thearticleEditpage and passes the id of the current row's entity as a parameter. This lets us navigate directly to the edit page for a specific article. - The second
GenericCellincorporates aDeleteEntityButton. This allows users to delete a specific article directly from the data grid. - We're using the
shrunkproperty on bothGenericCellcomponents. This keeps these cells as small as possible, ensuring that they don't take up unnecessary space in the data grid. - We've also added a new
LinkButtoncomponent to theActionsslot. This button links to thearticleCreatepage, allowing users to create a new article directly from the data grid.
Now, with these additions, our data grid is more functional, providing quick access to both editing, creating and deleting articles.
Add pages to side menu
The final step is to add our pages to the sidebar navigation. This provides easy access to all of our pages:
import * as React from 'react'
import { Menu } from '@contember/admin'
export const Navigation = () => (
<Menu>
<Menu.Item>
<Menu.Item title="Dashboard" to="index" />
<Menu.Item title="Articles" to="articleList" />
<Menu.Item title="Create new article" to="articleCreate" />
</Menu.Item>
</Menu>
)
Here's what this code does:
- We create a new
Navigationcomponent in theadmin/componentsdirectory. - We use the
Menucomponent from@contember/adminto build a sidebar menu. - Inside this
Menu, we create threeMenu.Itemcomponents. Each of these represents a link to one of our pages. The first item leads to the "Dashboard", orindexpage. The second item leads to the "Articles", orarticleListpage. The third item leads to the "Create new article", orarticleCreatepage.
And that's it! You have just created a simple data model and created custom interface, so you can edit the data.